Digitalization for Circularity in the Built Environment
Anna Batallé Garcia is a PhD researcher at the Department of Management in the Built Environment (MBE). In collaboration with her supervisors Prof.dr.ir. Ulrich Knaack from Architectural Engineering (AET) and Prof.dr. Paul Chan and dr. Tong Wang from MBE, she is exploring the potential of digitalization to support circular flows of materials in the AEC sector. With a focus on the façade industry, her research aims to learn from current industry forward processes to establish a systematic approach towards deconstruction and disassembly of façade components enabled by digitalization. In this video, Anna introduces the concepts of digitization and digitalization while presenting examples that explore the integration of several digital tools to shift the current paradigm towards a Circular Built Environment.
Main Takeaways
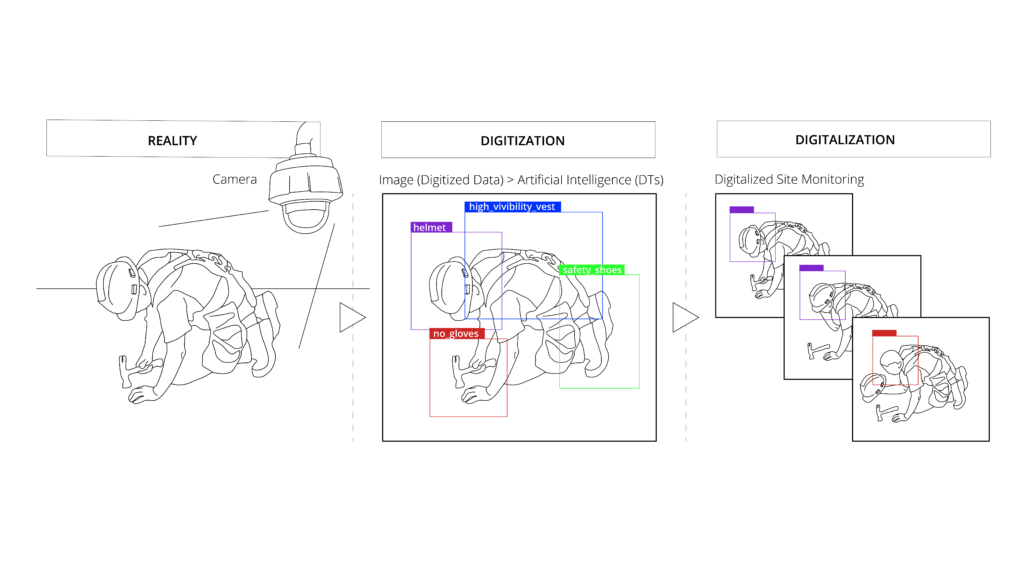
- Digitization is simply the process of converting physical data, also referred to as analog data, into a digital format.
- Digital Tools (DTs) refer to the various technological solutions that enable us to collect, share, analyze, and automate data.
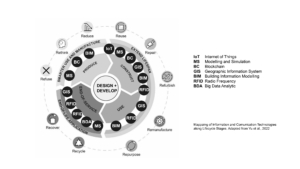
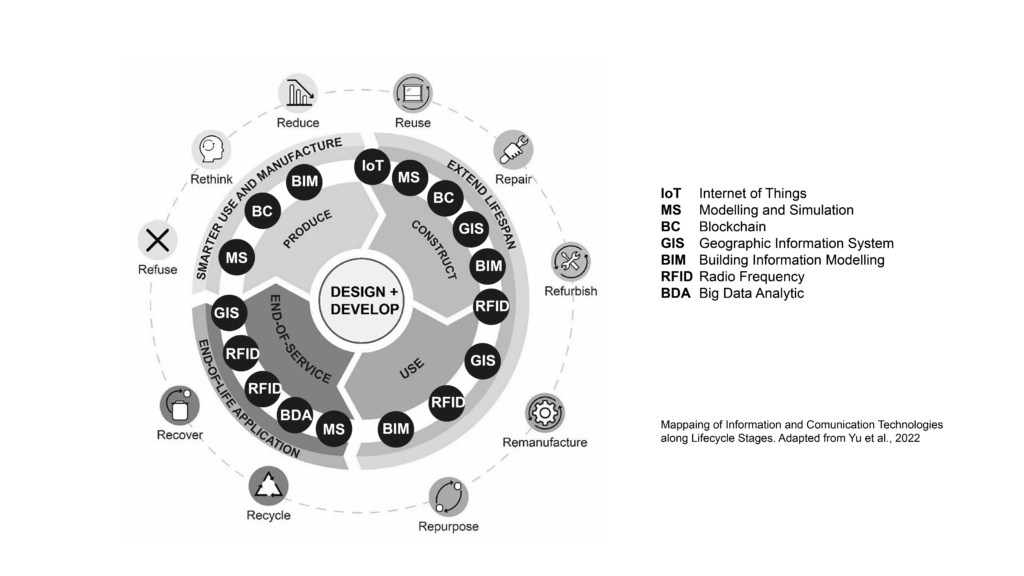
- Digitalization can be understood as the application of Digitized Data, and Digital Tools to impact how processes are performed. Digitalization can help us address many of the challenges we face when trying to transition towards a more circular economic model.
- Digitalized workflows can consist of several stages and depending on their scope, employ different digital tools. As research continues to advance and refine digital tools, it is essential that we understand how we can combine them to create integrated approaches that streamline current circular processes, paving the way for a circular built environment.
Further Reading
Literature Reviews on Digital Tools for a CBE
Çetin, S., De Wolf, C., & Bocken, N. (2021). Circular Digital Built Environment: An Emerging Framework. Sustainability, 13(11), 6348. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116348
Liu, Q., Trevisan, A. H., Yang, M., & Mascarenhas, J. (2022). A framework of digital technologies for the circular economy: Digital functions and mechanisms. Business Strategy and the Environment, 31(5), 2171-2192. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3015
Yu, Y., Yazan, D. M., Junjan, V., & Iacob, M.-E. (2022). Circular economy in the construction industry: A review of decision support tools based on Information & Communication Technologies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 349, 131335. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131335
Chen, Q., Feng, H., & Garcia de Soto, B. (2022). Revamping construction supply chain processes with circular economy strategies: A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 335, 130240. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130240
Digitalised Workflows for CBE
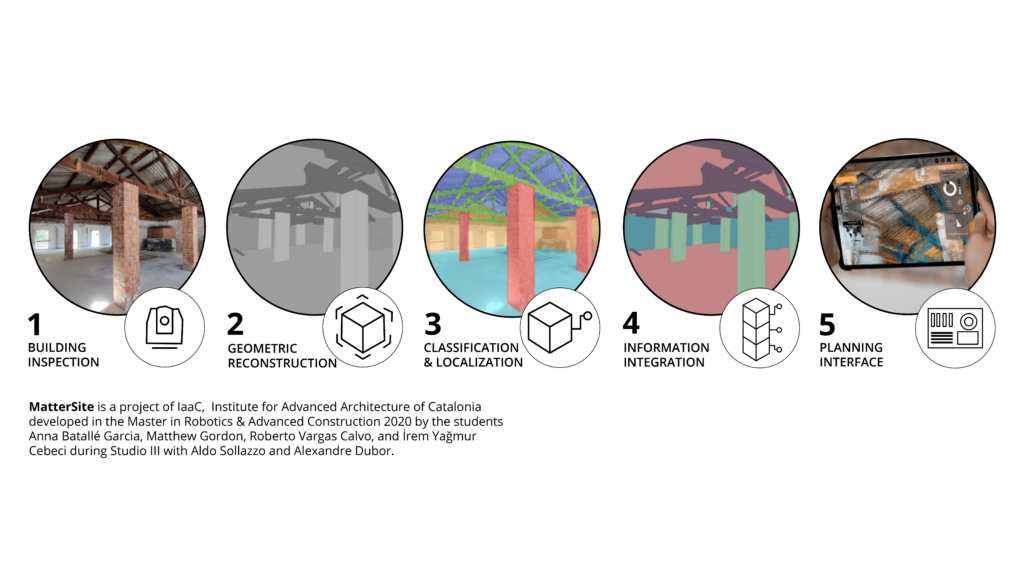
Gordon, M., Batallé, A., De Wolf, C., Sollazzo, A., Dubor, A., & Wang, T. (2023). Automating building element detection for deconstruction planning and material reuse: A case study. Automation in Construction, 146, 104697. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104697
Çetin, S., Gruis, V., & Straub, A. (2022). Digitalization for a circular economy in the building industry: Multiple-case study of Dutch social housing organizations. Resources, Conservation & Recycling Advances, 15, 200110. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcradv.2022.200110
Platforms and Projects Discussing CBE
Digital Circular Lab. https://www.dice-lab.com/
Digital Deconstruction. Advanced Digital Solutions Supporting Reuse and High-Quality Recycling of Building Materials